Remote Panel Features
The main control panel is the “Remote Panel” which provides easy access for adjusting the imaging conditions (Channels) and executing the acquisition Protocols. The Remote Panel is usually visible and provides the most commonly used control-set for acquiring multi-dimensional image data.
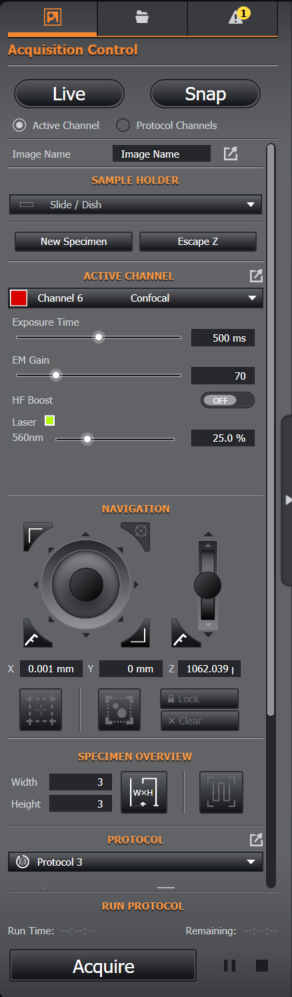
ACQUISITION CONTROL
Live: acquire a live image into the window on the left hand side of the application. Select the Active Channel radio button to acquire using the Channel specified in the ACTIVE CHANNEL dropdown and Protocol Channels to acquire a Live multi-channel image using the Channels defined in the Protocol.
Snap: acquire a single or multi-Channel image using the Active or Protocol Channels.
ACTIVE CHANNEL: dropdown to select the desired Active Channel – it does not have to be a Protocol Channel, but it makes sense to use one of those! For Live imaging and setup we recommend using the longest wavelength for minimal photo-toxicity. You can quickly adjust settings of the active Channel here, such as Exposure Time, Laser power etc.
NAVIGATION: the joystick provides a “proportional” control of the XY stage, while the arrows around the control provide movement in eight directions. The triangular button on the bottom left of the control switches the jog movement from Coarse to Fine. The jog moves by half of one field of view (adjusted to system magnification) in Coarse and one tenth of the field in the Fine setting. These controls are described in the Specimen Navigation section.
Specimen: On this control you will find the tools to help you load a New Specimen: such as Escape the objective to a safe position and Refocus the objective once the specimen is loaded onto the stage. Once the specimen is refocused you can reset the Bounds or continue to use the existing Bounds of the previous specimen.
Set Bounds: Provides a tool to set limits (Bounds) on the microscope stage, therefore constraining navigation to a set area. This can be done at low or high power (magnification). Typically the Bounds are set to a rectangle defined by the top left and bottom right of the specimen area, usually within a cover slip in a dish or on a slide. The Bounds can be Locked and Cleared. As well as XY Bounds you can also set the Z Bounds, which determine the maximum Z and minimum Z values (excluding the Escape position). The maximum Z position is, where possible, inherited from the microscope control unit and stops the microscope focus drive from crashing the objectives into the specimen. This is especially important for short delicate and expensive high NA lenses, which tend to have short working distances in the order of 200-300 nm. For longer working distance objectives, the maximum Z serves to protect the objective from damage, but also sets the highest penetration of the focal plane into the specimen for deep imaging in thick specimens. The minimum Z limits will normally set the focal plane to just below the specimen cover slip: this simplifies the task of finding focus, which can be tricky for high NA objectives and in confocal and TIRF imaging modes, where optical sectioning can be extremely strong.
Position Definition: Position Definition allows the user to setup a list of fields for observation.
PROTOCOL: The protocol section of the panel provides a summary of the key protocol information for that protocol type - such as the scan start and end points, Z position, mode and step settings. You are able to quickly change between different protocols, or access the protocol settings to make further changes. In addition you can run the protocol and view a summary of the progress.
To find out how to use the acquisition features please refer to the section Image Acquisition.